Exempt vs. non-exempt employees: Navigating worker classification
Higginbotham
MARCH 28, 2024
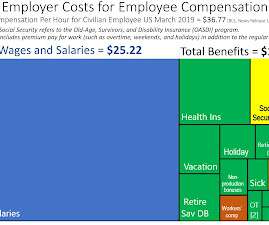
Such positions often require a salary that meets or exceeds a specific threshold rather than hourly pay. These workers are usually paid hourly and are eligible for overtime pay and minimum wage protections due to the nature and hours of their work. Such disputes often involve exempt and non-exempt employee classification requirements.












Let's personalize your content